Free Google Ads Tutorial for an absolute beginner covering campaigns and their types, networks, keywords, extensions, & answering common faqs

Google Ads (Formerly known as Google Adwords) is Google’s advertising platform for advertisers to display their ads on Google search engine results page and Google’s other sites like YouTube and Gmail and Google partner sites (Via Google Adsense).
Google Ads work in a real-time bidding environment where advertisers bid for ad placement on the search results page. However, there is a learning curve to using Google Ads, but they are very effective and can he;[ you get instant results. One can start generating sales in less than an hour.
For each keyword, there is a quality score for the ad. Depending on the maximum amount an advertiser is willing to spend, the adposition can vary, provided the quality score for the competing ads are equal.
If an ad’s quality score for a particular keyword is low, the amount that one may need to pay to show the ad can increase considerably.
Basic Terminologies
But before we get into the details of Google Ads, let’s first revisit some of the basic terminology used in the digital advertising world.
Google Campaign Types
Google Ads offers many different types of campaigns. So let us discuss each of them one by one.
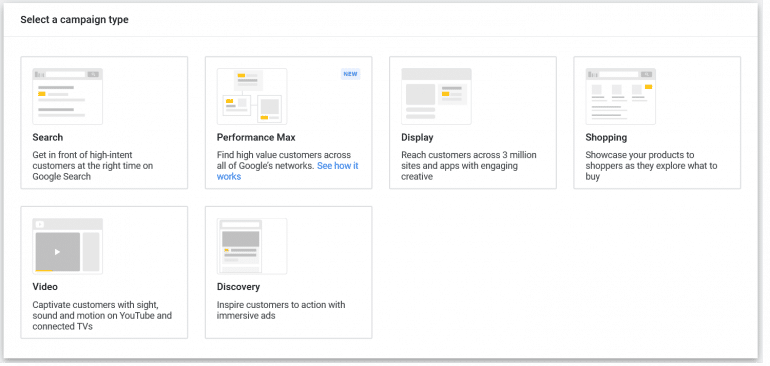
Search Campaigns
The ads appear on Google Search Engine Results Page (also known as SERP). The ads are targeted with keywords, and Google determines which ads to show based on the search term entered by the user, the quality score of the ad as well as the budget of the advertiser.
Display Network Campaigns
The ads that appear on Google’s display network can be in the form of banners or even text ads. In addition, the size of the ad can vary based on the position and placement available in different sizes.
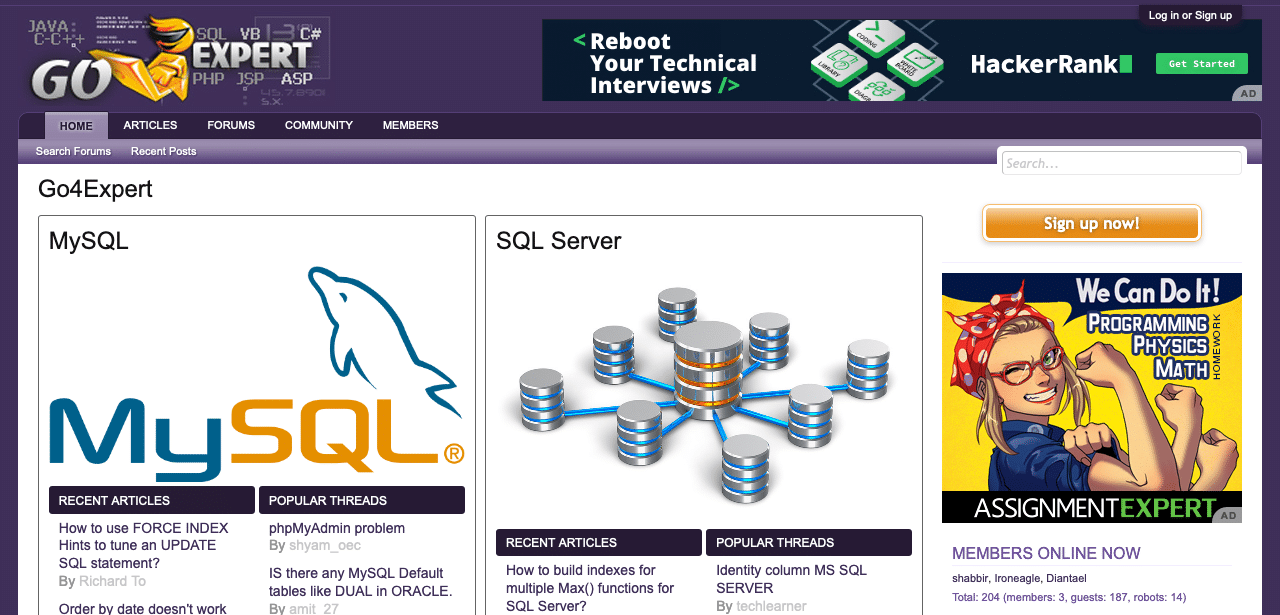
Any webmaster (person who owns a website) can apply to be part of Google’s partner network if the site complies with Google’s content guidelines.
Discovery Ads
Discovery ads allow you to take advantage of Google’s AI to deliver ads to the people inside the home newsfeed on the Google app. Further, the discovery ads also appear on YouTube’s home page, GMail Pages etc.

In short, when Google has no keyword data, Google displays discovery ads.
Video Ads
Video Ads allow your ads to display on YouTube. There are many types of video ads that you can run on YouTube, including skippable instream video ads, non-skippable instream ads, bumper ads, discovery ads, etc.
Video ads have a high Return on investment (ROI) for brand building.
Retargeting Campaigns
Have you ever wondered how you see the ads or price drops for the exact products you viewed on a particular e-commerce site?
The answer lies in the fact that e-commerce sites have created re-targeting campaigns.
Retargeting means targeting customers who visited your site or showed interest in your products or services but didn’t purchase them.

Shopping Campaigns
Shopping campaigns are created by pulling data from advertisers websites using an API or feed. If you want to create a shopping campaign, you have to provide the shopping related data to Google using the XML file or a CSV file. You can do that via Google’s merchant centre. Check out the official guidelines from Google here for feed format.
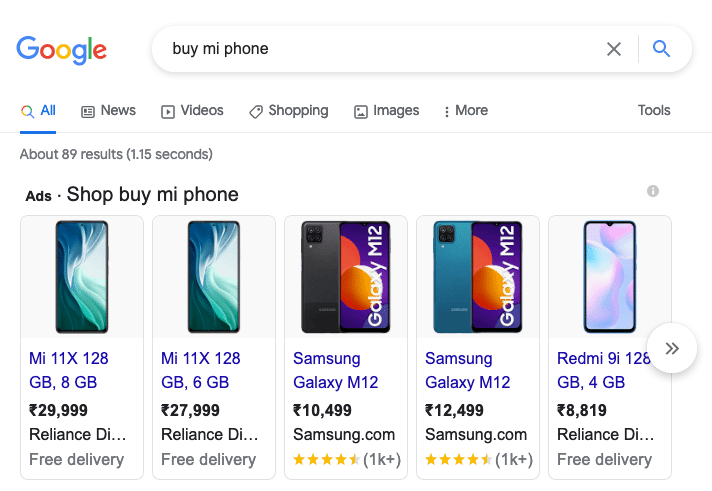
Types of Google Ads
Till now, we have seen the advertisers point of view for ads. Now we will see the types of Ads that a potential customer sees on Google.
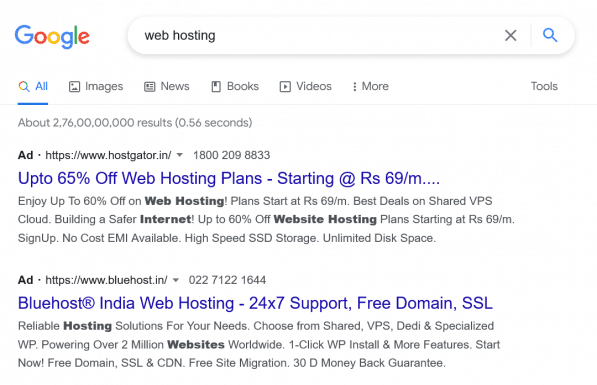
Text Ads
The ads appear on Google Search Engine Results Page (also known as SERP). The ads are targeted with keywords, and Google determines which ads to show based on the search term entered by the user, the quality score of the ad as well as the budget of the advertiser.

Text Ads with Extension
Text Ads can have extensions. There are many types of extensions that Google supports. For example, sitelinks, Call, Callout, and Lead form extension.
The example you see in the image below is the sitelinks extension where the link that says customer success story is also an ad and not an organic result.
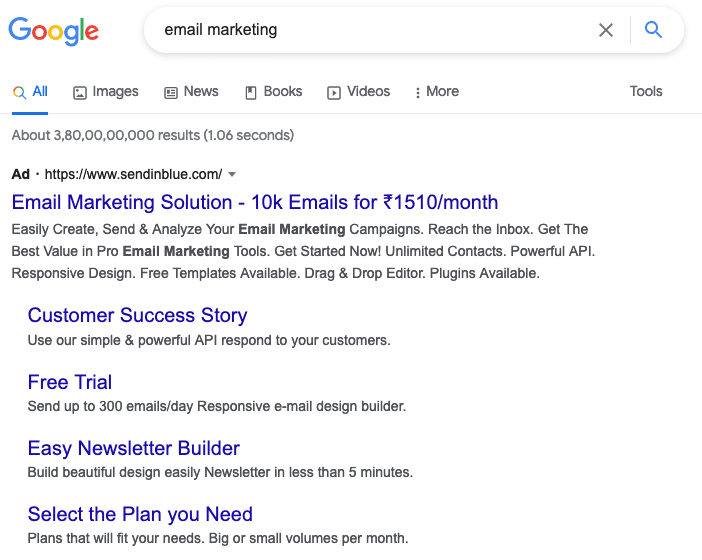
Similarly, in the web hosting search example above, the phone number that you see is a call extension from the advertiser.
Image Ads
Google Ads accept image ads, and they do not appear on the Google website directly but only on third-party websites via Adsense and Google network sites like YouTube. We target the placement via display network campaigns, and so they are also known as display ads.

Video Ads
Ads that you see on YouTube are video ads. YouTube also has text and discovery ads, but video ads are primarily skippable and non-skippable or bumper ads that play before or between the videos.

Responsive Image Ads
Do you notice that Image ads change shape and size when watched on a mobile device? They are responsive ads.
Responsive ads are the ones that can adapt to the size and shape based on the devices.

For example, the above ad on mobile devices may be vertical instead of horizontal.
Shopping Ads
Shopping ads are via shopping campaigns. You can even show your sites shop organically via Google’s merchant centre.

Call Ads
Call ads are via a call extension, and whenever a user clicks the ad, instead of taking the user to any website, it opens the mobile phones call interface with the number prefilled for the user to make the call.
Lead Ads
The lead extension helps you create a lead form to directly connect a webhook to get the user added to your CRM.
Note: you will need a total of $50,000 or equivalent in total spend to be eligible for a lead form.
Dynamic Search Ads
Dynamic Search Ads creates the ad’s title using the content from the landing page on your website.

Example: You own an international hotel chain. Someone searching on Google for “luxury hotel New York” sees your ad with the headline “Luxury hotel – NYC,” clicks your ad, and then lands on the page of your site that’s dedicated to your New York luxury locations.
Google Ads Bidding Options
Manual Cost Per Click (CPC)
Manual CPC bidding is one of my favourite strategies on Google Ads. Adjust bids for different ad groups or placements manually.
A way for an advertiser to monitor campaigns, ad groups, keywords and ads that are profitable or making a loss. It gives more control to advertisers. However, it needs daily monitoring to stay within the line of the daily budget.
Maximize Clicks
Setting up maximize clicks as a bidding strategy will give tons of clicks within the daily budget. In addition, it is an intuitive way to bid for lower competition keywords.
In short, one can get as many clicks as possible on their ads in a set budget daily.
Enhanced Cost Per Click (ECPC)
In enhanced cost per click, Google alters the bid for some keywords at some time on the lower side and others on the higher side to automatically manage the overall cost one is willing to pay for the click.
The system increases or decreases the bid amount depending upon the probability of a conversion.
CPM Bidding (Cost Per Thousand Impressions)
CPM is purely paying Google based on the impressions.
For obvious reasons, this bidding strategy is not for the search network. It is for display networks and YouTube campaigns only.
vCPM Bidding (Cost Per Viewable Impressions)
vCPM is for display networks or youtube text ads. An advertiser sets up a maximum cost for a viewable thousand impressions in this bidding technique.
Viewable impression means the ad is either loaded in the user viewport or is visible either because of the scroll or above the fold. You don’t pay if the ad is loaded in the footer and no one has seen it.
CPV Bidding (Cost Per View)
Cost-per-view bidding is only for video advertising on Google Ads. In CPV bidding, an advertiser pays for video views or interactions. Here, the definition of view (duration) is how long a viewer watches a video ad.
A view counts when a viewer watches a video for 30 seconds or more. It starts by entering the maximum cost-per-view an advertiser is willing to pay for a view or interaction.
Target CPA (Cost Per Acquisition)
Target CPA, aka Cost Per Acquisition, is for optimizing conversions. Suppose driving conversions is an advertiser’s primary goal, select target CPA bidding. What CPA does is focus on converting users within specific acquisition costs.
One crucial point is that Google doesn’t charge advertisers for action or acquisition. The model is primarily CPC only, but it adjusts the cost per click value such that you as an advertiser can achieve a targeted cost per acquisition.
Target ROAS (Return On Ad Spend)
Google ads will set bids to maximize conversion value based on the return on ads spend (ROAS).
So if I need 4x returns on my ad spending, it needs to have conversion value metrics first. Then it can have the target ROAS of 400% like
Sales (Rs.2000) / Ad spend (Rs. 500) x 100% = 400% is your ROAS
Maximize Conversions
When an advertiser sets maximum conversions, Google will automatically run ads to get the most conversions for the daily budget.
Again, remember that Google never charges for the conversion but only for the click but helps you achieve maximum conversions.
Target Search Page Location
The TSPL (Target Search Page Location) bidding strategy is all about getting on the first page of Google SERPs. Google will auto adjust bids to show ads on either the first page or top of first-page search results.
If an advertiser plans to use TSPL bidding, the ad score must be high quality. Otherwise, the budget will overshoot drastically.
Target Outranking Share
An advertiser will have to choose a website or competitor to outrank in this bidding method.
What happens is Google will increase bids to show your ads by outranking your competitor’s ads. Additionally, Google will show your ads when your competitor isn’t showing up.
Remember, your pay per click will go high if you decide to outrank a high bidding competitor.
Target Impression Share Bidding
When you want to have the most significant ad impressions, this ad strategy focuses on reaching out to maximum users.
For instance, you are an eCommerce seller selling cosmetic items. And you want your ads to show up 100% of the time for specific keywords. So, by selecting 100% as your target impression share, your ads will dominate the search results.
This bidding strategy can elevate your daily ad budget.
Google Ads Targeting Options
Targeting and audience segments
Location
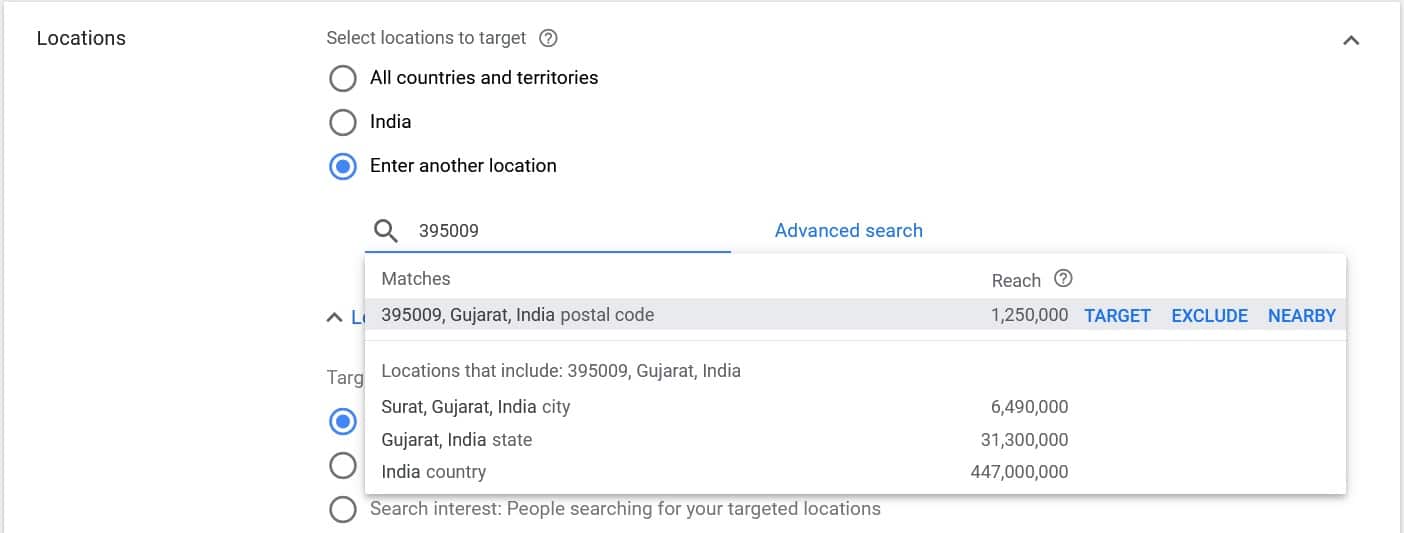
You can target an area based on
- Where they’re likely to be located or are located
- The places they’ve shown interest in
Similarly, you can exclude locations based on any of the above criteria
Languages
Select the languages your customers speak.
Audience segments
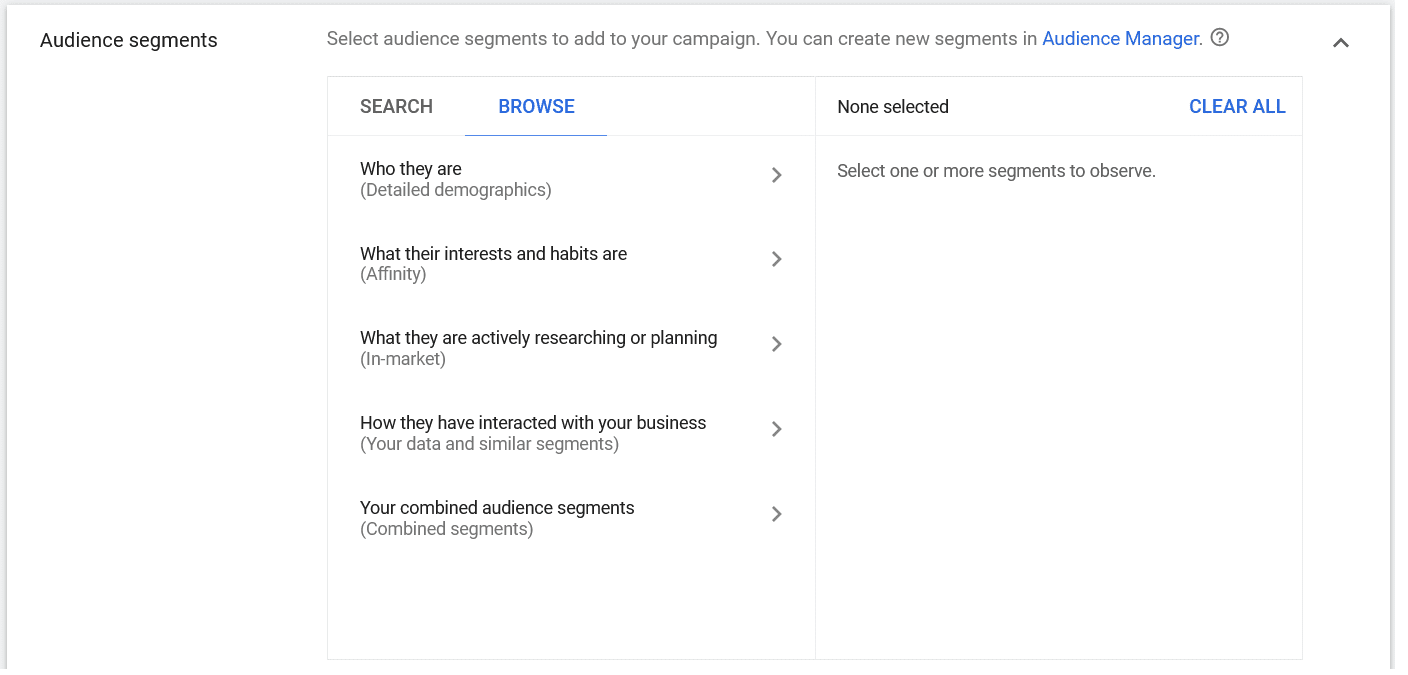
- Who they are – Age, Gender, Household Income.
- Interests and Habits – Business, Finance, Marketing.
- Actively searching or Planning – Restaurants, Clothes, etc
- Interact with your business – re-target

